Fax: 770-339-9804
Lawrenceville, Georgia 30046
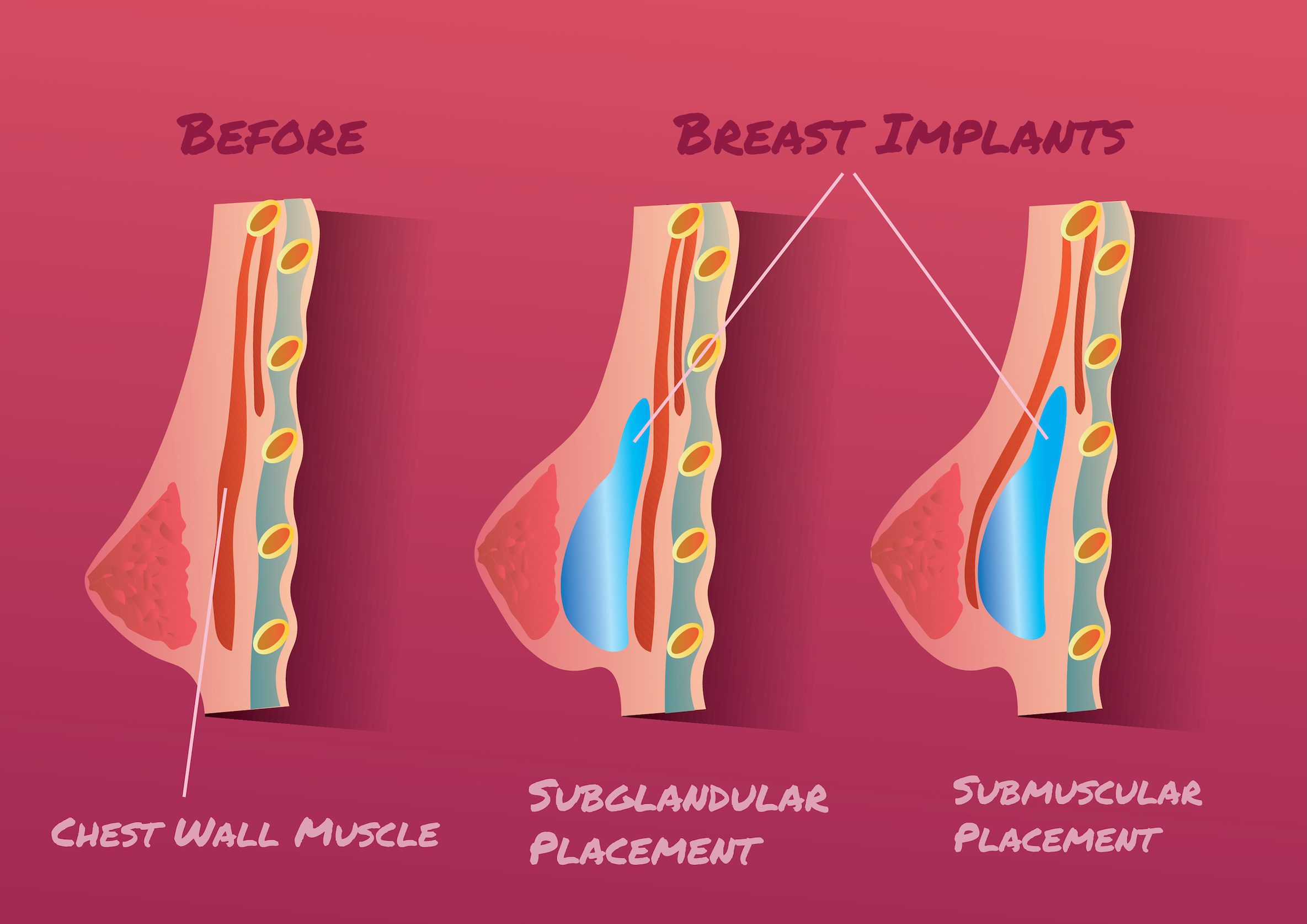
When undergoing breast reconstruction after a mastectomy, one of the most significant decisions you’ll make with your surgeon is where to place the implant—above or below the chest muscle.
Both options have their advantages and drawbacks, but in many cases, especially after mastectomy, placing the implant above the muscle (prepectoral) often yields more natural-looking and comfortable results.
Let’s dive into why this choice is critical and what factors to consider when making your decision.
The positioning of the implant—whether it’s above the pectoral muscle (prepectoral) or below it (subpectoral)—impacts various aspects of breast reconstruction, including recovery time, long-term aesthetics, and overall comfort.
For patients who have had a mastectomy, especially those who have lost all their breast tissue, the traditional submuscular (under the muscle) approach can create an unnatural appearance. In such cases, there is little to no natural tissue left to provide a smooth transition over the implant, which can result in an overly “stuck” look, with the implant being compressed behind the muscle.
Conversely, placing the implant above the muscle creates a more natural breast contour. This is particularly beneficial for patients undergoing post-mastectomy reconstruction, as the implant can better mimic the natural sag and movement of a breast.
In prepectoral implant placement, the surgeon places the implant directly on top of the chest muscle, within the existing skin envelope, and sometimes uses an acellular dermal matrix (ADM) or similar material to support and secure the implant.
In submuscular implant placement, the surgeon creates a pocket under the pectoralis major muscle to house the implant. This method has been widely used for breast reconstruction and augmentation, but it may not always be the best choice, particularly for post-mastectomy patients.
For many patients, especially those undergoing post-mastectomy reconstruction, the above-the-muscle (prepectoral) approach offers a more natural and comfortable result. The surgery is less invasive, recovery is quicker, and the final aesthetic can be more in line with the natural movement and aging of a breast. Moreover, this approach avoids complications like animation deformity and can be ideal for patients with thin skin or little natural breast tissue.
If your doctor mostly recommends above-the-muscle placement, it’s likely because they have seen better outcomes for their patients, especially after mastectomy, where there is no remaining tissue to cover the implant. This placement allows for a more natural look and feel while also making recovery easier and less painful.
Ultimately, the decision to place implants above or below the muscle should be made in consultation with your surgeon. Factors like your body type, the amount of natural breast tissue, lifestyle, and aesthetic goals all play a role in determining which option is best suited for your reconstruction.
Above-the-muscle placement may provide a more natural, comfortable result for many patients, especially those undergoing reconstruction after mastectomy. On the other hand, submuscular placement may still be a good option for those who need extra tissue coverage or want to minimize the risk of capsular contracture. Discuss all your options with your surgeon to ensure you make the choice that aligns with your needs and goals.
Schedule your consultation today at My Breast Cancer Doc to discuss your options. Call us at 470-322-6757 to book your appointment.